Control a serial RS-232 device over TCP sockets using an arduino ethernet board
Proposed here is an arduino-based converter that uses a TCP socket to send and receive commands to and from a serial device.
This allows legacy serial devices to be placed on a TCP/IP network.
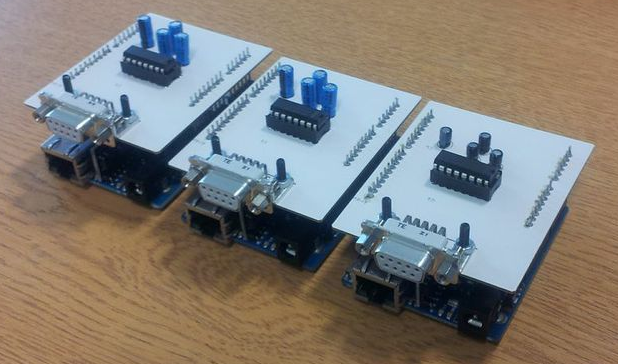
BoM
- 1 x Arduino Ethernet
- 4 x 1uF capacitors
- 1 x MAX232 IC
- 1 x Female 9-pin d-sub I/O
- 1 x 16way IC socket
- Board to board headers
- Stripboard
- Various lengths of wire
- An FTDI cable
A note on logic levels
The arduino uses a hardware interface, called a UART, to control serial data. The input/output of the UART is typically located on pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). The method of serial transmission used by the arduino is at the TTL level, such that a logic high (1) is given by $V_{cc}$ and a logic low (0) by 0V. RS-232 is similar, except that the ranges of voltages used to represent the data are different. A 0 is conveyed by a negative voltage anywhere between -3 and -25V, and a 1 by a positive voltage anywhere between 3 and 25V. To interface between these two signals, one must first invert and regulate them. This can be done using a MAX232 IC.
Arduino sketch
The following is an example sketch. Note that it may be required to change serial parameters e.g. baud, parity depending on the device that it is used to control.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
// ethernet
byte mac[] = { 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF };
byte ip[] = { 150, 200, 200, 200 };
byte gateway[] = { 150, 200, 200, 1 };
byte subnet[] = { 255, 255, 255, 0 };
// serial connection
int serialBaud = 9600;
int serialCfg = SERIAL_7O1;
// socket parameters
int serverPort = 8888;
// start TCP servers
EthernetServer server(serverPort);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(serialBaud, serialCfg);
// open serial communications
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip, gateway, subnet);
// start the Ethernet connection
server.begin();
// begin listening for TCP connections
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
}
void loop() {
// listen for incoming clients
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
String clientMsg ="";
while (client.connected()) {
// transmit
while (client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
clientMsg+=c;
// store received chars up to newline
if (c == '\n') {
Serial.print(clientMsg);
// then send the message through serial
clientMsg = ""; Serial.flush();
}
}
// receive
int incomingByte = 0;
// for incoming serial data
while (Serial.available() > 0) {
// if data has been received from the serial connection
incomingByte = Serial.read();
client.print(char(incomingByte));
// print the char data back to the client
if (char(incomingByte) == '\n') client.flush();
}
}
}
}